D2 Supreme
Description
Chemical Composition
| C | SI | MN | P | S | CR | MO | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.018 | 0.002 | 8.00 | 2.10 | 0.32 |
Standards
| JIS | DIN | BOHLER | HITACHI |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC53 | 1.2990 | K340 | SLD MAGIC |
Properties
- Higher hardness (62-64 HRc) than D2 after heat treatment.
- Twice the toughness of D2 with superior wear resistance.
- Substantially higher fatigue strength compared to D2.
- Smaller primary carbides than D2 protect the die from chipping and cracking.
- Secondary refining process (DLF) reduces impurities.
- Machines and grinds up to 40% faster than D2.
- Less residual stress after wire EDMing.
Applications
- Stepped punch and press-punching dies
- Concrete sprayer parts, rotor plates
- Swaging dies and backers
- Dies for cold forging
- Thread-rolling circular dies
- Piercing punch
- Thread-rolling dies for heat-treated bolts
- Forming dies
- Stripper plates for lead frame blanking
- Gauges
- Screws for injection molding machines
- Plastic Molds
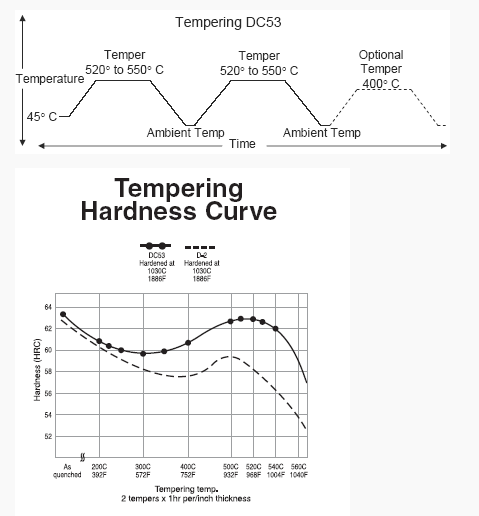
Tempering – Tempering is commonly performed in a non-atmosphere controlled convection furnace. The first temper should be conducted as soon as the part can be handled at about 45° C (120° F) to 65° C to (150° F). The part should be allowed to cool to ambient temperature between subsequent tempers.
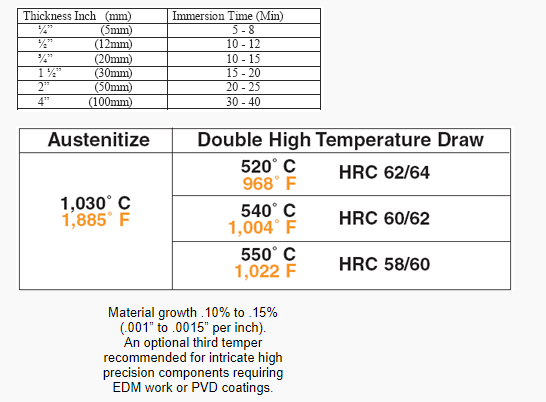
To achieve HRC 60-62, temper DC53 twice at 540° C (1,005° F) for 60 to 90 minutes per inch in thickness in cross section. The minimum tempering time is 90 minutes. Temper twice at 520° C (970° F) for the same amount of time to achieve HRC 62-64. A hardness less than HRC 60 is not generally recommended for most punch and die components due to insufficient compressive strength typically needed for stamping applications. Applications requiring additional toughness can be double tempered at 550° C (1,020° F) to achieve HRC 58-60.